BACKGROUND INFORMATION
The mass of a star is the amount of material it is made up of. The mass of the Sun is 300,000 times the mass of the Earth. But the Sun is only a medium sized star. It will live for about 10 billion years. Right now it is about 5 billion years old.
Stars less massive than the Sun are cooler, and they live longer. Stars more massive than the Sun are hotter, and they live shorter lives.
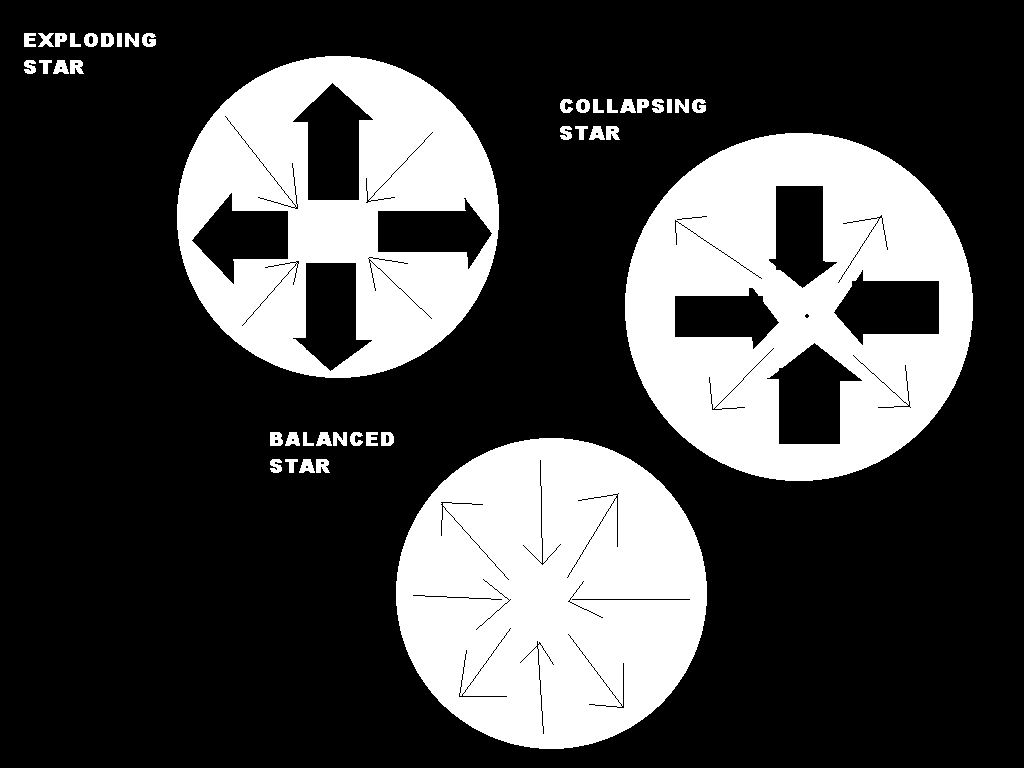
Our Sun is in balance. That means that it is not a collapsing star or an exploding star. A star in balance has energy made by the high temperature inside (energy that pushes out) equal to the gravitational energy (energy pulling inward).
If the force pulling inward becomes stronger than the energy made by the temperature on the inside, a star collapses because of gravitational contraction. Then the star heats to very high temperatures.
If the force shooting outwards is greater than the gravitational pull, the star expands, or maybe explodes. The exploding stars are novas or supernovas.

In 1987, Ian Shelton (an astronomer) was photographing Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC). This is a galaxy pretty close to our galaxy, the Milky Way Galaxy. It is only 170,000 light-years away. His photographs showed a star brighter than the whole galaxy. He thought maybe something was wrong with the photograph, so he went outside and looked at LMC. He even saw it just looking up into the sky.

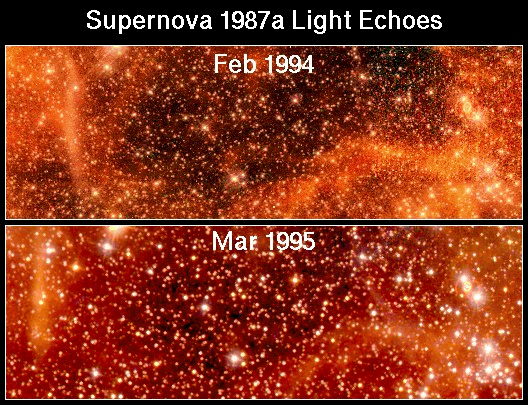
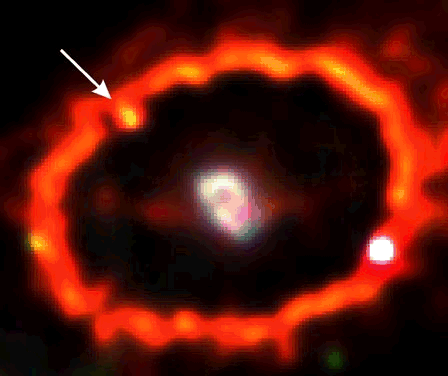
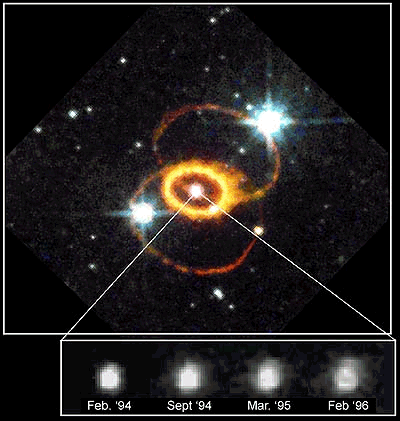
The star he was seeing was a supernova. It was the brightest supernova seen in 383 years. It is named Supernova 1987A because it was the first supernova seen in 1987. Usually it is called SN 1987A.
 | |
 |  |
 |
Novas are stars that suddenly become very bright, giving off more energy than they used to. Supernovas give off much more energy than novas. Astronomers have seen several hundred supernovas. Many are not so bright, because they are in very distant galaxies. In our galaxy, before SN 1987A there were four famous ones. They were so bright, people could see them even during the day. All of them were seen before the telescope was invented. The telescope was invented in 1609.
In 1006 A.D. a supernova was seen in the constellation Lupus, the Wolf. Records show us that people from China, Japan, Egypt, and southern Europe saw it.
In 1054 A.D. the Chinese saw a supernova in the constellation Taurus, the Bull. Today we cannot see the star, but if we used a telescope, we would see a huge gas cloud where the star once was. This gas cloud is called the Crab Nebula.
In 1572 A.D., Tycho Brahe, an astronomer from Denmark saw a supernova in the constellation Cassiopeia, the Queen.
In 1604 A.D., Johannes Kepler, an astronomer from Germany saw a supernova in the constellation Ophiuchus, the Serpent Bearer.